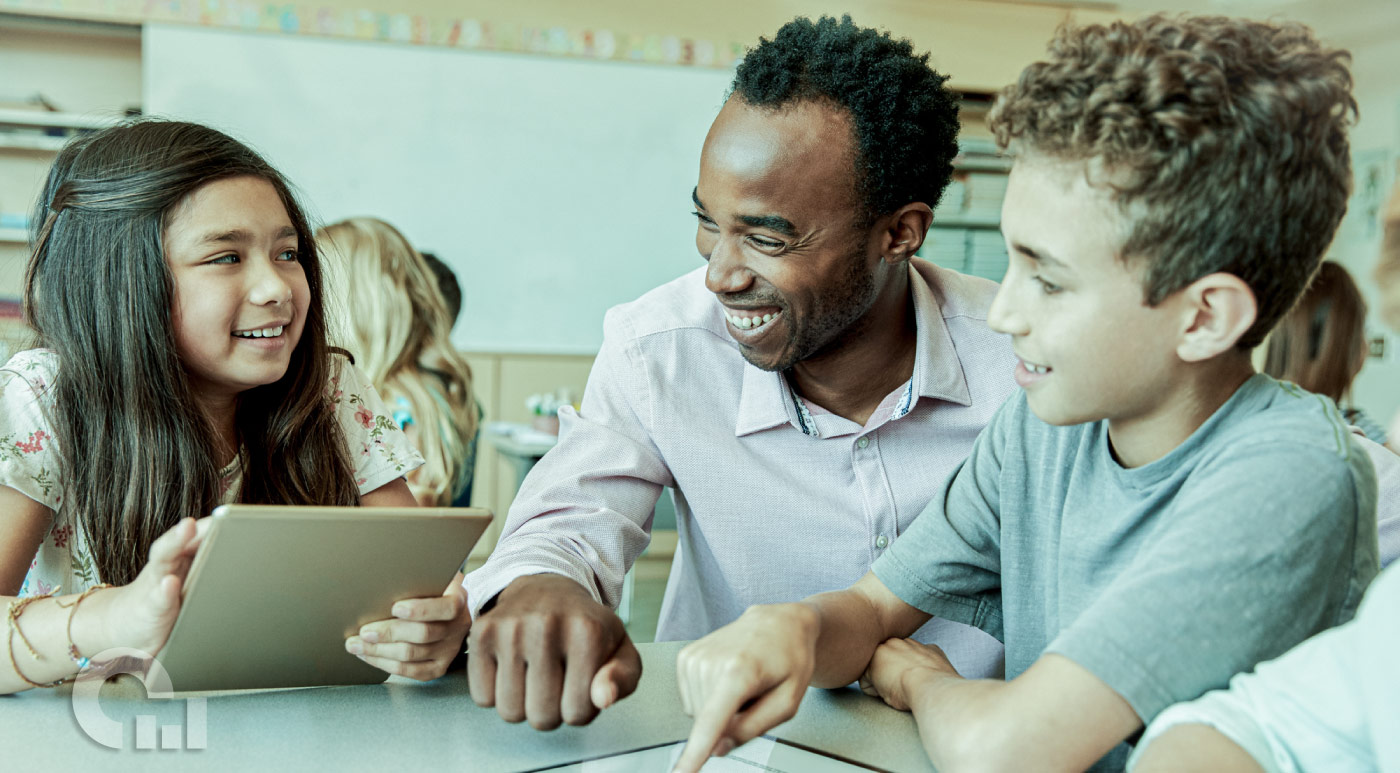
Becoming a teacher is a lifelong dream for many, but many current teachers need to continue their education. Earning one of the best master’s degrees in education can allow you to pursue new career prospects or progress up the educational hierarchy.
 Alternatively, many current teachers earn master’s degrees for the simple reason that those holding them earn more than teachers with just a bachelor’s degree.
Alternatively, many current teachers earn master’s degrees for the simple reason that those holding them earn more than teachers with just a bachelor’s degree.
Whatever your reasons, you can find lots of affordable online master’s in education programs. Yet finding the best online master’s in education programs is no easy task. Imagine spending all that time researching school after school and not knowing for certain if an institution is right for you.
Fortunately, we’ve already compiled the top schools for those seeking an affordable and flexible online experience as they complete a master’s degree in education. Let’s examine this degree and see where you can earn one with the best bang for your buck.
What is a Master’s in Education Degree?
A master’s in education degree is a progression of a bachelor’s degree in education or a related field. Those who earn this degree will learn more about the art of teaching and the development of education curricula. It’s very similar but distinct from a Master of Teaching degree.
The difference is that a Master of Education degree is a progressive certification that may lead to further schooling and focuses on curriculum and administration. In other words, this degree is a great choice for future school principals, counselors, or other school staff. While those with a Master of Education can also (and often do) continue to teach, that position is not all they can pursue.
A Master of Teaching, on the other hand, is a terminal degree and intended only for those who want to remain in the classroom for the entirety of their careers.
A master’s in education can come as either a Master of Science or Arts. Both degrees will teach you more advanced topics concerning teaching students and the development of curriculum, with slight differences in the course lists or focuses of the program depending on whether it’s an MS or MA. Some Master of Education degrees enable you to pick a concentration or focus, though this is not usually in a subject like you would with a Bachelor of Education. Instead, the concentration will be on things like administration, curriculum, school functions, or similar emphases.
How Much Can You Earn with a Master’s in Education Degree?
The potential earnings for those with a master’s in education degree are high. As we discussed, most people pursuing these degrees want to enter school administration and curriculum development rather than remain a classroom teacher for the entirety of their careers.
Those with a master’s in education degree can become elementary, middle, and high school principals. This is a steady career option with about a 4% job growth rate over the next 10 years and an average annual salary of $95,310.
Alternatively, graduates can proceed to become a postsecondary education administrator. This position is similar to a principal in a regular school but instead offers administrative responsibilities for colleges or universities. Such administrators can become Deans or other high-ranking officials within a college network. This job growth rate is about 7% over the next 10 years according to the BLS, with an average annual salary of $94,340.
Of course, those with master’s degrees in education can still become or remain teachers. High school teachers earn an average annual salary of about $60,320 per year, but those with any kind of graduate degree are often paid much more than their peers. The upper limit for high school teachers is closer to $100,000 per year, making such a career quite lucrative indeed.
You can alternatively become a college teacher or work in some kind of postsecondary educational institution. These professors usually make about $78,470 per year. Unlike regular teachers, those with more experience and higher degrees can earn much more than teachers who only hold a bachelor’s degree in a given subject. The highest pay cap for postsecondary teachers is closer to $175,000 per year.
Overall, the opportunities for advancement and financial security are many for those with master’s degrees in education.
What is Required for a Master’s in Education Degree?
Those who study for a master’s in education will have to tackle a variety of comprehensive and often interdisciplinary topics and classes. Because these degrees are focused on the theory of teaching and school administration in addition to practical applications of teaching skills, these programs are arguably more diverse and abstract than Master of Teaching programs.
In these programs, you’ll have to complete classes of subjects like:
- Psychology
- Communication
- English
- Curriculum
- Student Learning Theory
- Management
- Administration
- Finance
- Counseling
- Sociology
Ultimately, those with a Master of Education will become well-rounded individuals with a variety of useful skills that will make them attractive employees, both as advanced teachers and as school administrators. Such individuals will be able to demand a high price for their services and earn more than teachers with bachelor’s degrees only.
What Are the Best Master’s in Education Degrees?
We made it our goal to find the best master’s in education degrees for your convenience. To discover the 50 best online master’s in education degrees, we relied on comprehensive data from several sources.
OSR uses six data points: three school-wide and three program specific. For school-wide, OSR uses Student Satisfaction, Admission Rates, and the number of programs the school offers online. For program-specific, OSR checks the Median Debt of graduates from that program, how many degrees are offered within that program’s umbrella department, and what percentage of students at that school graduated from that department. These numbers are self-reported by colleges to the US Department of Education.
The six statistics are displayed by each school. The sliding bar under each statistic represents how that school compares to other US institutions. “Not reported” means a school did not release that information to the Department of Education. A more detailed description of the OSR process can be found on the methodology page.