Imagine a world where you can make an excellent salary, have a flexible work schedule, access plentiful opportunities, and pave the way for the next generation of human intelligence.
Wouldn’t that be a perfect world? Thankfully, this world already exists under the guise of computer science.
From rundown garages in Silicon Valley to the skyscrapers of Bangalore, computer science is shaping our world. Everything digital revolves around computer science experts and the work that they do. They’re the inventors, innovators, and engineers who have built the figurative house in which most of us live and work.
Computer science may seem like a difficult sector to absorb and enter, but it’s more accessible than you’d think. In this guide, we’re going to teach you everything you need to know about the field, from possible careers to degrees.
See Also: How Hard is it to Get a Job in Computer Science?
What Is Computer Science?

Computer science is the study of information in all of its digital forms. From storing digital information to trading and creating it, computer scientists use algorithms, programming languages, and systems to innovate and design our world.
Steve Ballmer, the former CEO of Microsoft and the current owner of the Los Angeles Clippers, once said, “Computer science is the operating system for all innovation.” Let’s consider his statement by looking at some of the most significant innovations of the last two decades: social media platforms, smartphones, autonomous vehicles, and search engines. If you took computer scientists out of the woodwork, none of those technologies would exist.
Computer science is a massive field. Some subfields of computer science are cryptography, data science, computer graphics, numerical analysis, software engineering, and human-computer interaction. These studies only comprise a small percentage of computer science subfields.
Really, computer science is so vast that it would take hours to explain all of its aspects. To learn more about the technical aspects of the sector, take a glance at the free courses on Stanford Engineering Everywhere and MIT OpenCourseWare. Each of these websites offers dozens of classes that focus on the fundamentals and innovations of computer science.
There are many ways to learn computer science. Some of the leading computer scientists of today are self-taught, with no university experience or other formal education. But these people form the margin of computer scientists. Because the field is growing more and moee competitive, you should find every way to get ahead of your competition, and that includes university.
Graduating from an associate or bachelor’s program in computer science will give you the knowledge and network needed to advance in the field. Some people continue on to obtain a master’s degree, which provides computer scientists with even more experience, education, and qualifications than their competition. More still are so fascinated with computer science that they become theoreticians and professors through doctoral programs rather than practitioners.
Careers in Computer Science
Again, there are dozens of professions within the computer science field. From Software Developers to Information Security Analysts, every aspiring computer scientist has more than enough room to find their niche. In the chart below, we’re going to analyze five popular computer science jobs, the education required to get those positions, and the average mid-career salary for each subsector.
| Job Title | Approx. # Years of Education | Average Annual Salary |
| Software Developer | 4 | $105,590 |
| Database Administrator | 4 | $93,750 |
| Computer Programmers | 4 | $86,550 |
| Computer and Information Systems Managers | 4 | $146,360 |
| Computer Systems Analysts | 4 | $90,920 |
All salary data is courtesy U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics Occupational Outlook Handbook.
Software Developer

Software development is perhaps the most robust and plentiful profession in the computer science sector. Software developers design computer science applications, recommend software upgrades to existing applications, create innovative software, and design programs according to the needs of consumers.
There are two essential kinds of software developers. The first, applications software developers, design all types of computer applications. Some of these professionals design the apps we use on our phones, such as Uber, Tinder, Instagram, and WhatsApp. Other applications software developers focus on creating databases that organizations use to store, document, and transfer data.
Secondly, there are systems software developers. These developers create, update, and re-design operating systems of all kinds. Some examples of operating systems are Windows 10, macOS, Android, and Linux. These operating systems are consumer-focused, but systems software developers also design operating systems that support businesses. Consumers and companies can use these systems to interact with their computers, phones, vehicles, and appliances.
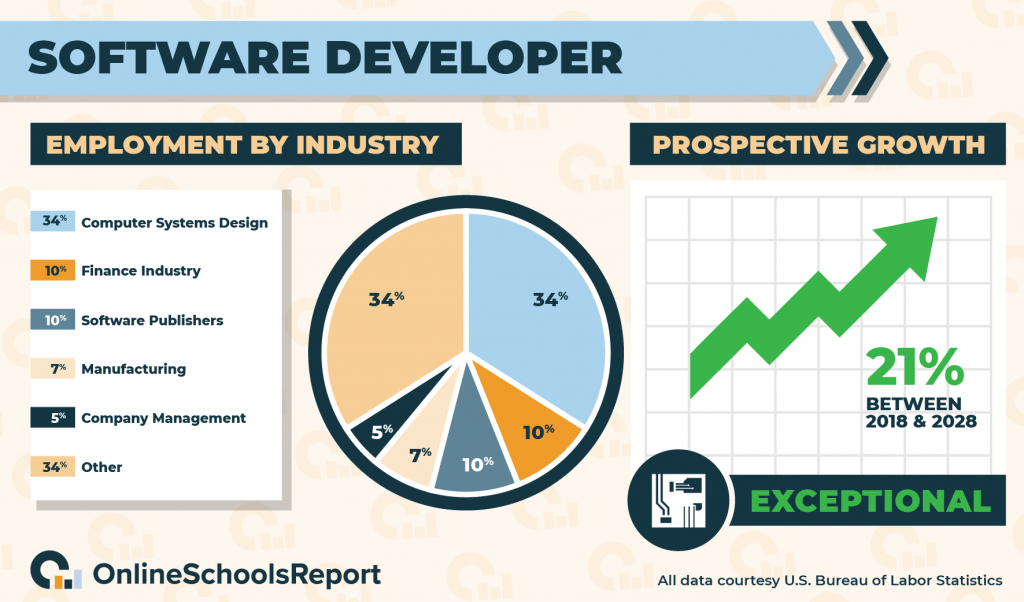
Software developers hold approximately 1,365,500 positions across the United States. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, 34% of them work for computer systems design and related services, 10% work in the finance industry, 10% work for software publishers, 7% work for manufacturers, and 5% work in company management.
Most software developers graduate from a bachelor’s program in computer science, software engineering, or a related field. Most graduate from computer science programs because of the degree availability and versatility. Some, however, choose programming degrees because of the importance of computer languages in the software development field.
To prepare for a career in software development, you should focus on gaining as much experience as possible. You should try to find internships and freelance work while you’re studying the craft, and you should always stay up-to-date on the latest innovations and programming languages.
Some employers seek software developers with a master’s degree. But if you don’t have an advanced degree, you still have access to many jobs. Software development is one of the fastest-growing computer science jobs; The Bureau of Labor Statistics forecasts that employment in the field will grow by 21% between 2018 and 2028.
Database Administrator

Database administrators are the backbone of our financial, commerce, and healthcare systems. They are the people tasked with storing, organizing, and securing the data of everything from small businesses to large institutions.
Some principal tasks of database administrators include merging databases of consolidating businesses, backing up and restoring data, ensuring that databases run smoothly, and modifying existing databases. One vital task of database administrators is to protect the security of both consumers and businesses, whose sensitive information may appear in databases.
There are two main types of database administrators: systems database administrators and applications database administrators. Systems database administrators install updates and troubleshoot databases, while applications database administrators write and debug programs using programming languages.
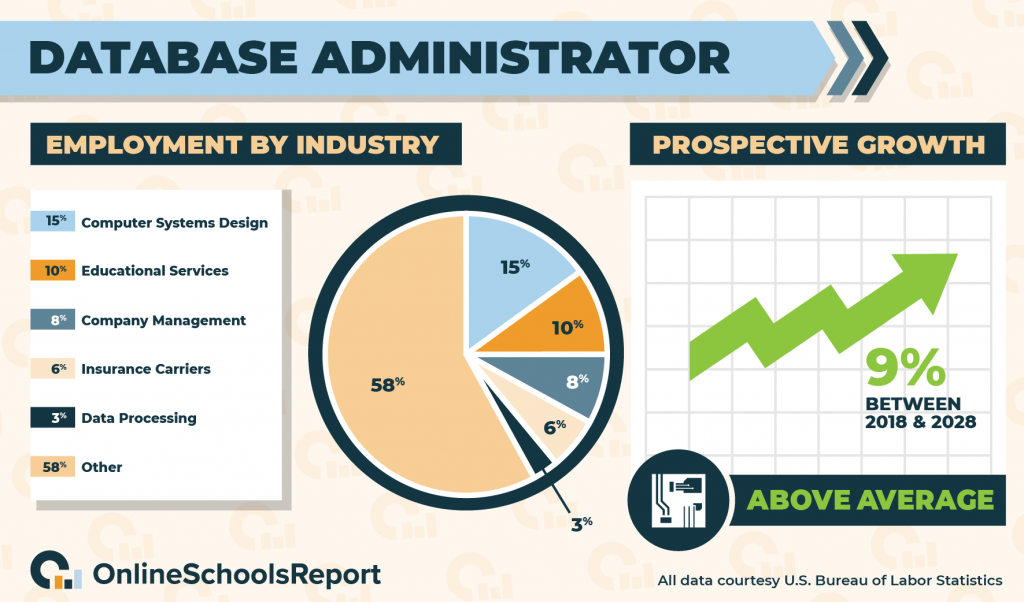
There are 116,900 database administrators (DBAs) across the United States, and the Bureau of Labor Statistics forecasts that this number will grow by 9%, or 10,500 jobs, between 2018 and 2028. According to the BLS, 15% of DBAs work for computer systems design and related services, 10% work for educational services, 8% work for company management, 6% work for insurance carriers, and 3% work for data processing, hosting, and related services.
Most employers prefer accepting DBAs who hold at least a bachelor’s degree. Applicants can prove their knowledge with undergraduate degrees in computer science, information systems, or information technology. Larger organizations and companies with extensive personal data in their databases often prefer hiring DBAs with a master’s degree.
Most aspiring DBAs must know a database language. The most frequently used language is SQL, but some organizations may use a similar but different language. Most university programs teach SQL, but if your program doesn’t, you can find many free sources for learning SQL online.
Computer Programmers
Computer programming is perhaps the most accessible field in computer science. While other professions require a diverse understanding of computer systems, computer programmers often need to know only one programming language to find a decent job. Computer programmers write applications in programs using computer languages like C++, HTML, Java, and XML. Additionally, they update existing programs, test programs for errors, simplify applications using code writing, and edit incorrect code in existing programs.
Software developers and computer programmers often work hand-in-hand in Agile, Waterfall, and other models. Software developers lay the groundwork and long-term vision for applications, while computer programmers work as the ground soldiers, writing and editing code.
Some programming languages, such as HTML and Java, are relatively simple to learn. Thus, jobs that require these languages may be challenging to obtain, as hundreds of thousands of people in the United States already know these languages. Jobs that require more challenging programming languages, like C++, however, are steady in demand.
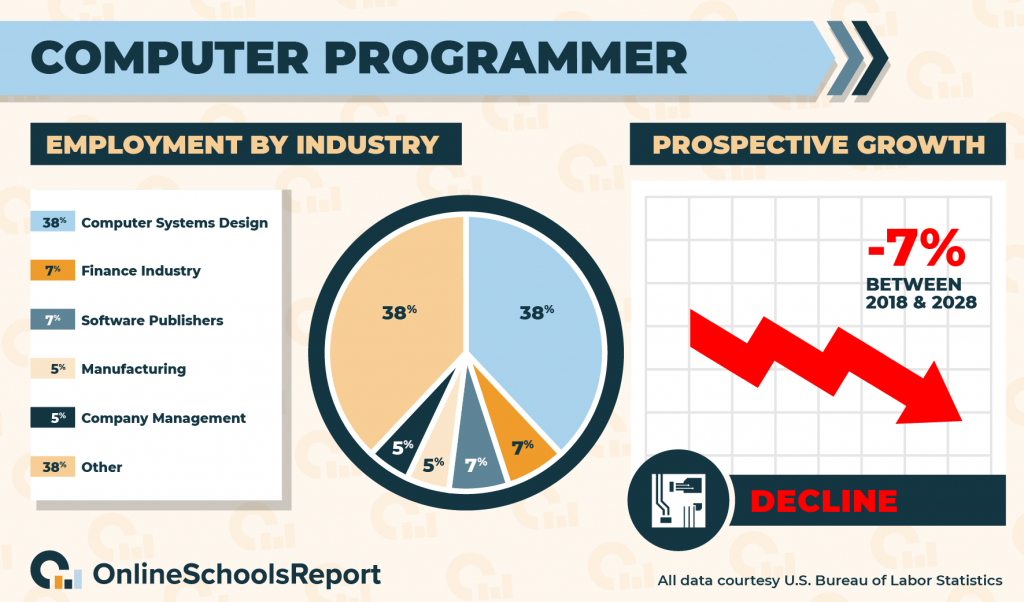
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, 38% of computer programmers work for computer systems design and related services, 7% work for the finance and insurance sector, 7% work for software publishers, 5% work for manufacturers, and 5% of workers are self-employed. You should take note of the prevalence of self-employed work. Unlike many computer science positions, there are often plenty of available freelance opportunities for computer programmers. People in this sector have pioneered the lifestyle of digital nomads, which allows you to travel while performing part-time freelance work.
Unfortunately, computer programmers are falling in demand. While there were 250,300 computer programmers in 2018, the Bureau of Labor Statistics estimates that this amount will drop by 7%, or 17,900 jobs, by 2028. You can still secure a job, though, if you have a resume that shows your expertise.
You can access this field with a bachelor’s degree, but many people break into a programming career with no formal educational experience. Many online websites like Coursera, Edx, and Udemy teach programming languages for a vastly reduced cost when compared to universities.
Computer and Information Systems Managers

Computer scientists make steady wages across the board, but who doesn’t want to climb the ladder toward more prestigious and lucrative positions? Near the top of the computer science ladder lies computer and information system managers. These are the people who oversee the computer science-based area of an organization.
Computer and information systems managers, also known as IT managers, oversee everything from hardware upgrades to internet security. They work on both the short and long-term needs of a department, ensuring that each project is running smoothly and efficiently. They also guide and assess computer programmers, software developers, and information security analysts.
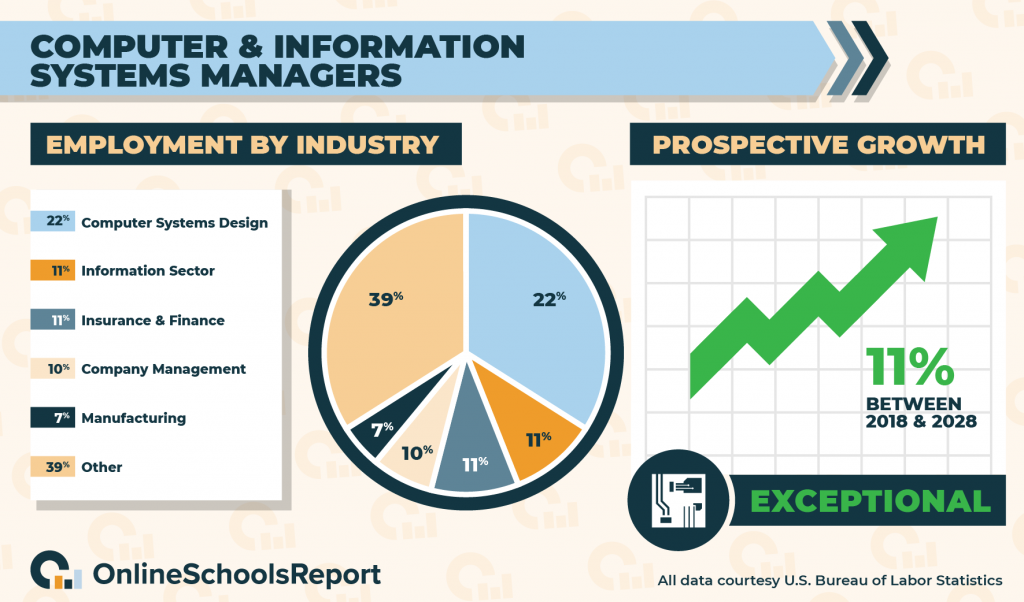
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, 22% of IT managers work for computer systems design and related services, 11% work for the information sector, 11% work for the insurance and finance sector, 10% work for company management, and 7% work for manufacturing firms. The BLS also estimates an 11% job growth between 2018 and 2028.
Technically, IT managers only need a bachelor’s degree. A person with a master’s or doctorate, however, may stand out when compared to other applicants. But the most significant factor of obtaining a management position is experience. Very few people can make the climb from university to a management position. It takes hard work, and you shouldn’t expect to reach this position in fewer than five years of professional experience.
Computer Systems Analysts

Sometimes, computer science extends beyond the IT or programming departments. Almost every worker in an organization uses a computer. Now, imagine that each person’s computer works 5% slower than the latest computer innovation. That means the organization’s output is at only 95% of its potential. For a large company, that 5% slowdown translates to a significant amount of time and money.
One vital role of computer systems analysts is to study the computer systems and procedures of a company and recommend changes when required. In the example given in the first paragraph, a computer system analyst may suggest that the organization updates to the latest computer innovation.
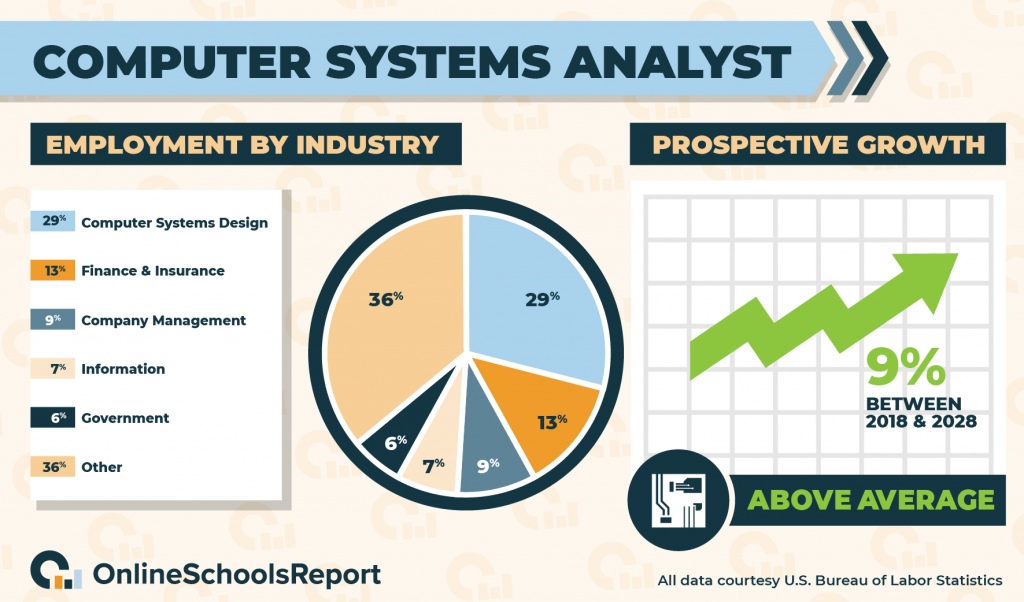
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, 29% of computer systems analysts work for computer systems design and related services, 13% work for the finance and insurance sector, 9% work for company management, 7% work for the information sector, and 6% work for the government. There’s also a 9% estimated job growth between 2018 and 2028, according to the BLS.
Most computer systems analysts have a bachelor’s degree in a related subject, but a degree isn’t required by every organization. Those who hold degrees usually have one in computer science, information technology, or a business-related field. A few of the top-ranking computer systems analysts have MBAs.
Part of the experience of being a computer systems analyst is continuing education. If you’re in the field, you must learn about the latest computer technologies, IT practices, and other technological advances. It also helps to have an intermediate understanding of the sector in which you work. If you’re working in the insurance sector, for example, you should understand the essential practices of the business.
Computer Science Degrees
Computer science is an umbrella term, and while you can find many general computer science degrees, you can also find many programs that are more specific and focused. Some examples include information science, software engineering, health informatics, computational science, and artificial intelligence. We recommend that students choose computer science as their major, though, unless they are confident that they want to work in a more specific field.
Associate’s Degree in Computer Science

You should consider an associate degree if you’re in one of two categories. The first category is for people who don’t want to invest in a college education. The truth is that university isn’t always affordable, and not wanting to accrue massive debt is an understandable decision. The second category is for self-taught computer scientists who are experts in the field, but who wish to supplement their knowledge with a formal degree.
If you’re interested in obtaining an associate degree in computer science, you may find programs at your local community college and university. There are many online options, too, for people who don’t want to commute or study in a formal setting. Some classes that students in an associate program may take are Introduction to Computer Networks, Computer Technology, and classes in specific programming languages.
Associate programs are typically the least demanding, quickest, and most affordable degrees to obtain. Given the two-year pathway of most associate programs, students usually don’t make their way to very specialized courses. There are exceptions, though: some computer science degrees focus on a specific subject, like Linux or Java. In these programs, students solely focus on learning about the programming language or operating system, becoming experts in the field.
To graduate from an associate program, students must complete two years of coursework with a 2.0 or higher GPA. Many schools require students to graduate with a 2.5 or 3.0 GPA, though, so always pay attention to the specific requirements of your program.
Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Science

A bachelor’s degree in computer science is the standard requirement for most positions in the field. You can secure a job with an associate degree, but those with an associate are at an inherent disadvantage compared to people with a bachelor’s or master’s. People interested in enrolling in a bachelor’s program can find one in state schools, online, or in one of the cheapest programs in computer science.
Some courses that students may take in a bachelor’s in computer science program are Software Architecture, Discrete Structures, Numerical Analysis, Introduction to Computer Architecture, and Computer Programming. Some of these courses provide foundational information, while others are more practical.
Bachelor’s degrees offer a few benefits when compared to associate programs. First, the extra two years of coursework provides the space to examine advanced subjects and develop a broader range of expertise. While an associate program may end at an intermediate level, bachelor’s programs look at many topics in-depth.
Second, bachelor’s programs also emphasize the liberal arts. While literary, history, and art courses may not seem relevant to you, they help teach students the art of learning. Moreover, they provide an alternative pathway for graduates who may seek an eventual career shift.
Master’s Degree in Computer Science

If a bachelor’s degree serves as a ticket into the computer science field, then consider a master’s program to be a golden ticket. Master’s programs provide in-depth education, proof of your expertise in the field, and the qualification to get almost any job you please.
Master’s programs in computer science usually range from 45 to 60 credits. Students take around two years to complete full-time programs and three to five years to finish a part-time master’s in computer science program. Students often choose an emphasis in a master’s program, such as Artificial Intelligence, Biocomputation, Computer Security, Information Management, Software Theory, and Theoretical Computer Science.
To enroll in a master’s program, students should have a bachelor’s degree from an accredited university and a GPA of 2.5 at the bare minimum. To graduate from a master’s program in computer science, students in the most demanding programs must have a 3.0 or higher GPA. There is no thesis requirement for most computer science master’s programs. Instead, students focus on coursework and occasionally complete a final project.
Learn more about master’s programs through our ranking of the Best Online Master’s in Computer Science. There, you can find the best and most affordable online programs in the country.
Doctoral Degree in Computer Science

Doctoral degrees in computer science are for people who are aspiring researchers and experts in the field. Gaining a doctoral degree isn’t required for any job besides a college professor or technical researcher. Thus, it isn’t necessary unless your aspirations lie in those two categories. But if you have the time and the fondness for education, a doctoral degree can act as a strong supplement to your resume.
Most doctoral programs take around five years to complete. Gaining admission to a doctoral program can be complicated. Aspiring students must demonstrate a research interest and provide evidence for the research they’ve already done. If aspiring students haven’t completed research yet, they should try to do so before applying in order to display their ability to research niche subjects.
Besides demonstrating research potential, aspiring students to doctoral programs must complete a bachelor’s degree, have two or three letters of recommendation, and submit GRE scores. Master’s degrees aren’t required, but they will help you gain admittance if your undergraduate degree isn’t in a related field.
As you may have guessed, doctoral programs are heavy on research. Students usually supplement their studies with an internship with leading technological companies. Many programs require students to choose a minor, too.